What are Browser Attacks & How to Avoid them [20 Different Types]
Prevent vulnerabilities that could compromise your data
- There are various browser attack types you can encounter depending on the components of your browser that are lacking.
- With an alarming increase in cybercrime, website security is critical. Updating your applications and software will help patch its loopholes and prevent cyberattacks.

There are countless browser attack types these days, and it isn’t uncommon for anyone to encounter them. Understanding what constitutes these attacks might be worthwhile considering the high cybercrime rates.
Usually, most browser attack types are geared toward exploiting vulnerabilities in the browser to gain information. This information can then be diverted or infected with malicious malware to cause data breaches or loss.
However, there are several ways of preventing these browser attacks. Today, we’ll go through the preventive measures and means of checking. However, before diving into this, let’s examine the popular types of web browser attackers that are common.
What is a browser attack?
In a browser attack, attackers find and take advantage of the security weaknesses in a browser or software. It can lead to the loss of valuable information and also money.
These attacks can make your PC and stored data vulnerable to editing, deletion, and even copying by third parties. This, in turn, can cause havoc in your personal life, as sensitive information like credit card details might be saved in the attacked browser.
Preventing this from happening will ensure that you can use your device on any browser without worrying about your data being stolen or copied.
Before we reach that part of our journey, let’s first look at what shape browser attacks take in day-to-day life.
What are the different types of web attacks?
1. What is a brute force attack?
It is a method of hacking that is very straightforward, and it is one of the simplest. The whole concept of brute force attack is trial and error.
The assailant forms passwords and login credentials by guessing. However, cracking passwords and encryption codes with brute force can take a long time.
It happens because the assailant needs to try countless probabilities before gaining access. Sometimes, it can be a futile effort to use the brute force attack, depending on how logical the password is.
2. What are active attacks?
An active attack happens when an infiltrator changes the data sent to the target. This attack uses compromise to deceive that target into believing he’s got the information.
However, the assailant interferes with the system or network by sending in new data or editing the target data.
An active attack can sometimes employ an attack known as a passive attack. This attack takes precedence over an active attack. It involves gathering information about the hacking, known as spying.
Also, hackers edit packet header addresses to redirect messages to their desired link. It gives them access to information going to someone else, such as account details and credentials.
3. What is a spoofing attack?
A spoofing attack occurs when an infiltrator pretends to be another person to have access to someone else’s data. This attack steals classified information, data, files, money, etc.
However, the victims must fall for the fake information for a spoofing attack. In short, spoofing is when a cyberattacker impersonates another person by sending simulated data for illegal access.
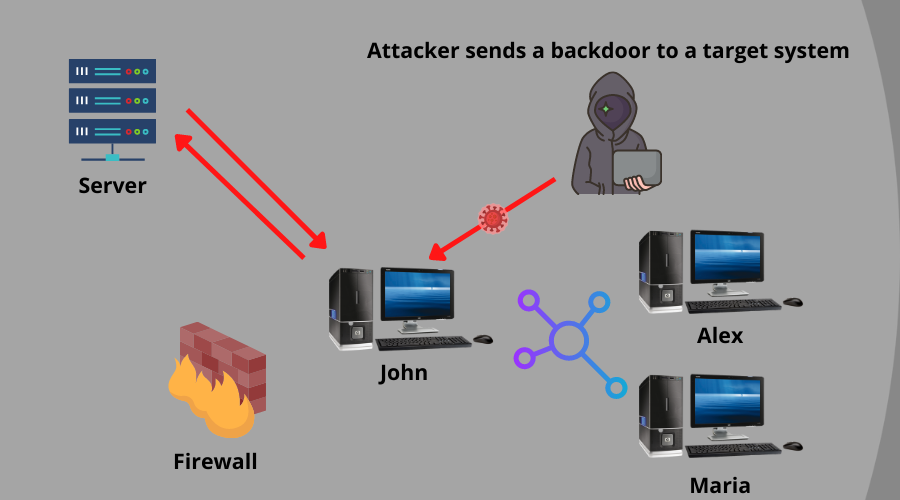
4. What is a backdoor attack?
A backdoor attack is when an attacker uses external agents like viruses or malware to penetrate the root of a system. Then, it targets the core parts of your system or application, like servers. Why they do this is to be able to bypass every security measure.
However, the concept is attacking the backdoor or backend will give you access to every other door before it. After the backdoor attack is successful, the infiltrators can control the whole system.
Malware like spyware, ransomware, and crypto-jacking are tools for this kind of attack. When malware is in the system or application, it will be possible for the attacker to break the security protocols.
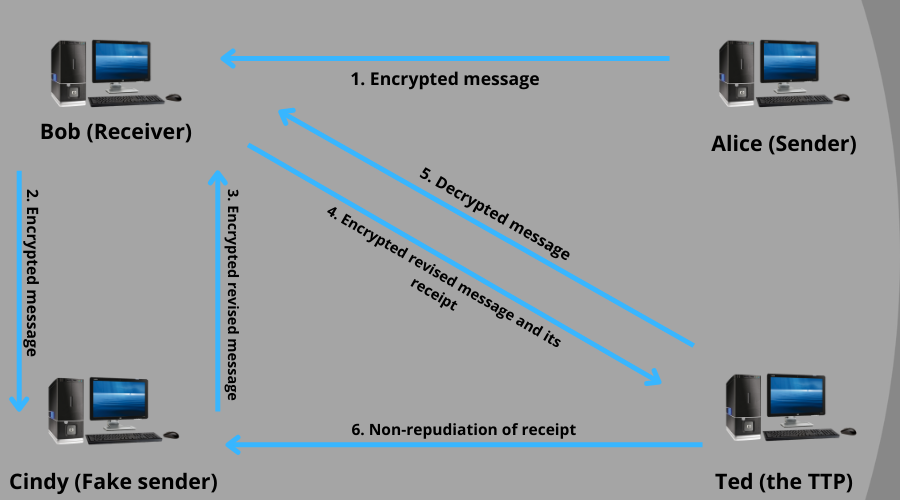
5. What is a repudiation attack?
This type of attack occurs when a user denies performing a transaction. The user can deny that he is unaware of any action or transaction. Therefore, it is necessary to have a defense system that tracks and records all user activities.
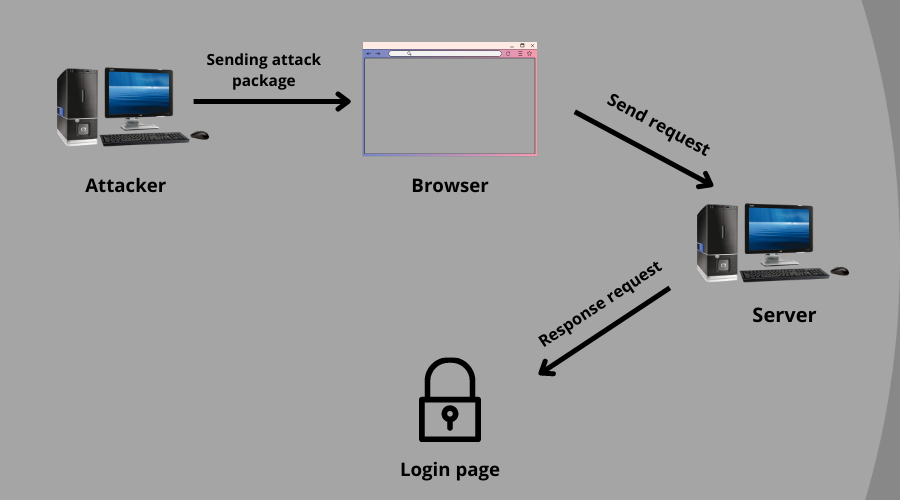
6. What is a Man-in-the-middle attack?
An example of a Man-In-The-Middle Attack is using public Wi-Fi. Assuming you connect to Wi-Fi and a hacker hacks the Wi-Fi, he can send malware to the connected targets.
As the name implies, this kind of attack is not direct. Instead, it comes between the client and the server like a middle-man. It is common for sites with no encryption on their data to travel from the client to the server.
Furthermore, it gives access to the attacker to read login credentials, documents, and bank details. The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate blocks this kind of attack.
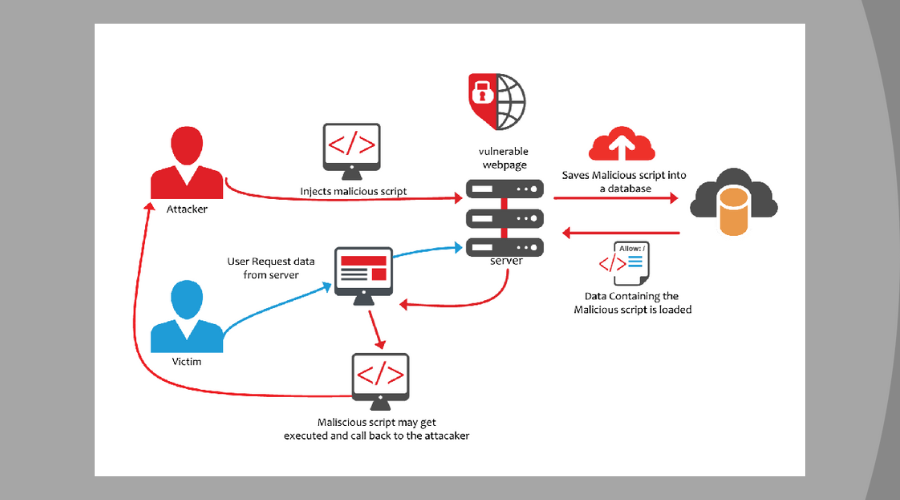
7. What is cross-site scripting (XSS)?
This attack targets the users who visit any website already infected with malware. The attacker infects the website with malicious code, then creeps into the site’s visitors system. This code allows the attacker to access the site and change website contents for criminal intentions.
8. What is a malicious browser plugins attack?
Plug-ins are small applications you download on your browser to add more features. If a malicious plug-in gets into your browser, it can go through your history and password chain. That’s why questions like whether BTRoblox is safe should always be on top of your mind before installation.
9. What is a broken authentication attack?
This type of attack hijacks user login sessions after a broken authentication session.
10. What is a SQL injection attack?
The hacker injects malicious codes into the server and waits for a victim to execute the code on their browser. It is a simple way for hackers to steal valuable data from your system.
11. What is a DNS Poisoning attack?
When a DNS Poisoning attack is injected into your browser, it’ll get redirected to a compromised website.
12. What are Social Engineering attacks?
This type of attack uses deceptive means to trick the user into performing actions that’ll be dangerous for them. An example is spamming and phishing. This method often focuses on presenting too much to be real opportunities as bait.
13. What is a botnet attack?
This type of attack uses devices you pair with your computer to get into your browser. Also, it gives them access to your whole system.
14. What is a path traversal attack?
Hackers inject disturbing patterns into the web server, giving them access to user credentials and databases. It aims to access files and directories stored outside the web root folder.
15. What is a local file inclusion attack?
This type of attack forces the browser to run a specific injected file that has been laced in the local file.
In case the assault is effective, it will disclose touchy data and, in severe cases, can prompt XSS and remote code execution.
16. What is an OS command injection attack?
This browser attack type deals with injecting an operating system OS command into the server. The server runs the user browser, so it is vulnerable, and the attacker can hijack the system.
17. What is a lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) attack?
This kind of software authorizes anyone to access the data in the system. However, if a hacker injects such software, he’ll be able to reach the data.
18. What is an Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) attack?
It is a browser attack-type of access control vulnerability that arises when an application uses user-supplied input to access objects directly via the browser. This involves the attacker manipulating the URL to gain access to the data on the server.
19. What is security misconfiguration?
There will be loopholes when developers make mistakes or omit some necessary changes. This security misconfiguration makes the browser vulnerable. Hence, it can leave the browser open to various attack types.
20. What is a Missing Function-Level Access Control attack?
Attackers exploit the weakness, which is the missing function. This kind of Missing Function Level Access Control gives the attacker access to classified data. Also, it allows them to exploit tasks that are not available to an ordinary user.
What are some measures you can take to help prevent web attacks?
➡ Always use strong passwords
It will be hard to infiltrate your data if you protect it with a strong password that intruders cannot decipher. The use of multiple characters, upper and lower case alphabets and numbers should be employed.
Another effective solution is the use of multifactor authentication. MFA allows you to protect your account with more authentication methods. So, peradventure a hacker cracks your password, and your account will demand additional proof.
➡ Make use of a random session key.
This kind of security allows you to generate new passwords and IDs for every session attempt. A random session key works like a token software that generates a new password for every transaction or login.
It will prevent intruders from accessing the previous session with the last login credentials. Additionally, this measure contains the session replay active attack.
➡ Use an Anti-Exploit Program
Anti-Exploit Programs protect your web browsers and software from misbehaving or giving room for threats. In addition, they strengthen the security system of your browser to fight the browser attacks trying to get in.
However, anti-exploit programs prevent external interference with your browser. These programs are good to run alongside an antivirus for more security.
➡ Be cautious of browser extensions
There are tools you can download on your browser for more productive features. However, some browser extensions can be malicious and dangerous for your browsers.
Carefully investigate the extensions you want to install on your browser to avoid detrimental effects.
➡ Use a 64-bit Web Browser
Browsers like Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge operate on 64-bit. They have strong protection and resilience against browser attacks. The 64-bit version web browser has an advanced security system preventing attacks.
➡ Install an Antivirus
Antivirus can help detect malicious activity and also prevent intruders into your system. Depending on how deep the security of the antivirus software goes, it contains software from penetrating your device.
Antivirus software will scan your device to detect malware and select them. There are lots of Antivirus software out there. Go to our page for the best antivirus for you.
➡ Keep your system updated
Browsers and software are always vulnerable one way or the other. It is why developers make updates to fix the loopholes in the previous version.
However, when your software is not up-to-date, it leaves room for attacks to penetrate your system. Hackers sneak through these vulnerabilities to exploit your data and access your account. Employ patch management software to keep your applications up to date.
➡ Use Wi-Fi security
Almost everybody in this present age connects to Wi-Fi every day. Unfortunately, it is dangerous because hackers can tap into the network. However, a security code on your Wi-Fi will prevent unauthorized persons from joining it.
What are the different types of web application attacks?
1. Injection Attacks
This type of web application attack affects the server’s database. The hacker will insert malicious code into the server, get access to user inputs and credentials, and allow modifications.
2. Fuzzing
Fuzzing is a type of attack that uses fuzz testing to find the vulnerability of the software. To find these loopholes, hackers input several corrupted data into the software to crash. Then, they use a fuzzer to detect where the loopholes are. These loopholes are the entry points for hackers to exploit the software.
3. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)
This type of web application attack temporarily renders the site inaccessible or offline. When you enter countless numbers of requests to the server at once, it will crash or become unavailable.
However, the DDoS attack does not inject malware into the system. Instead, it confuses the security system, giving the hacker time to exploit the software.
4. Using unverified code
Almost every piece of code has a backdoor that makes it vulnerable. If this is not well secured, a hacker can inject malicious code into it. Peradventure, such infected code is incorporated into your site, it will serve as an entry for attack.
5. Phishing
Phishing is a web application attack where a hacker pretends to be someone else. It is to get the victim to share important information and data. Assailants use spoofed emails to lure victims into the trap of sharing valuable information.
Preventive measures for web application attacks
- Always take your time to investigate emails and messages before replying or even opening them.
- Before implementing any code into your application, make sure your developers check. If there is a third-party code in the piece of code, remove it.
- Install a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate on your site. The SSL will encrypt data transfer from the client to the server and vice versa.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN). It monitors and balances the traffic and load that goes through sites.
- Install an Antivirus on your system to scan, detect, and delete malicious data.
Hackers are coming up with new ideas for infiltrating applications and software daily. So, you need to keep your security system up to date.
Browser attacks all have one thing in common, and it is the fact that they find weaknesses in software. These weaknesses give them access to exploit your system and steal valuable data. Following the measures mentioned above can help prevent web attacks.
If you want to know about the best antivirus software for your devices, we have an article about that. Also, you can check our page for details on the best anti-exploit tools to protect your browser from attacks.
Likewise, you can check our website for more browser attacks related issues and easy fixes for them.